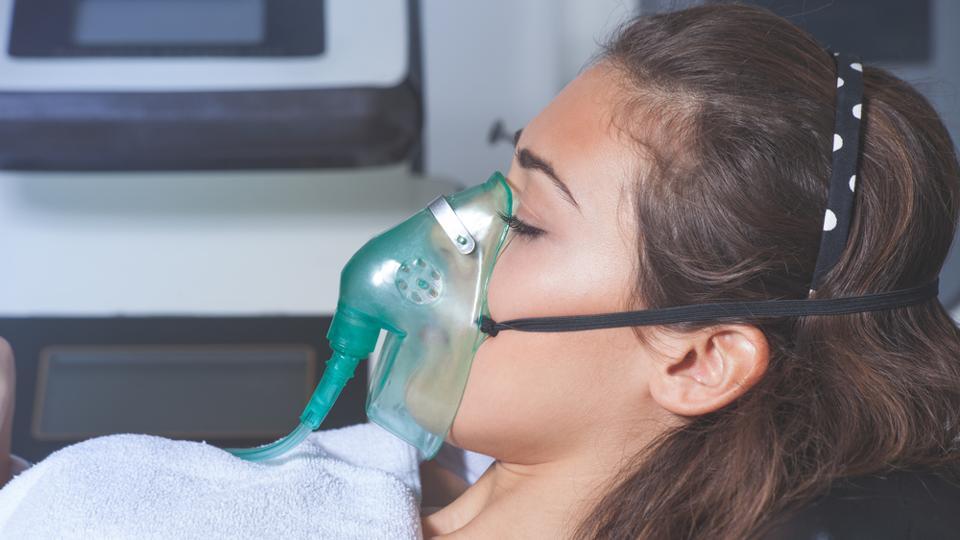
Oxygen is an essential element for humans and its deficiency can result in death in only a few minutes. Respiratory failure occurs when one or both gas exchange functions of respiratory system fails and this may indicate a condition called hypoxemia or hypoxia.
‘Hypoxia’ and ‘hypoxemia’ are often used interchangeably in some publications. However, they are different from each other in the medical world. Hypoxemia is a condition in which arterial tension or partial pressure of oxygen is below normal (i.e. below 80-100 mm Hg). And, hypoxia is deficiency of oxygen supply at tissue level.
Here are the causes, symptoms, preventions and treatment of hypoxemia and/or hypoxia.
Causes Of Hypoxemia/Hypoxia
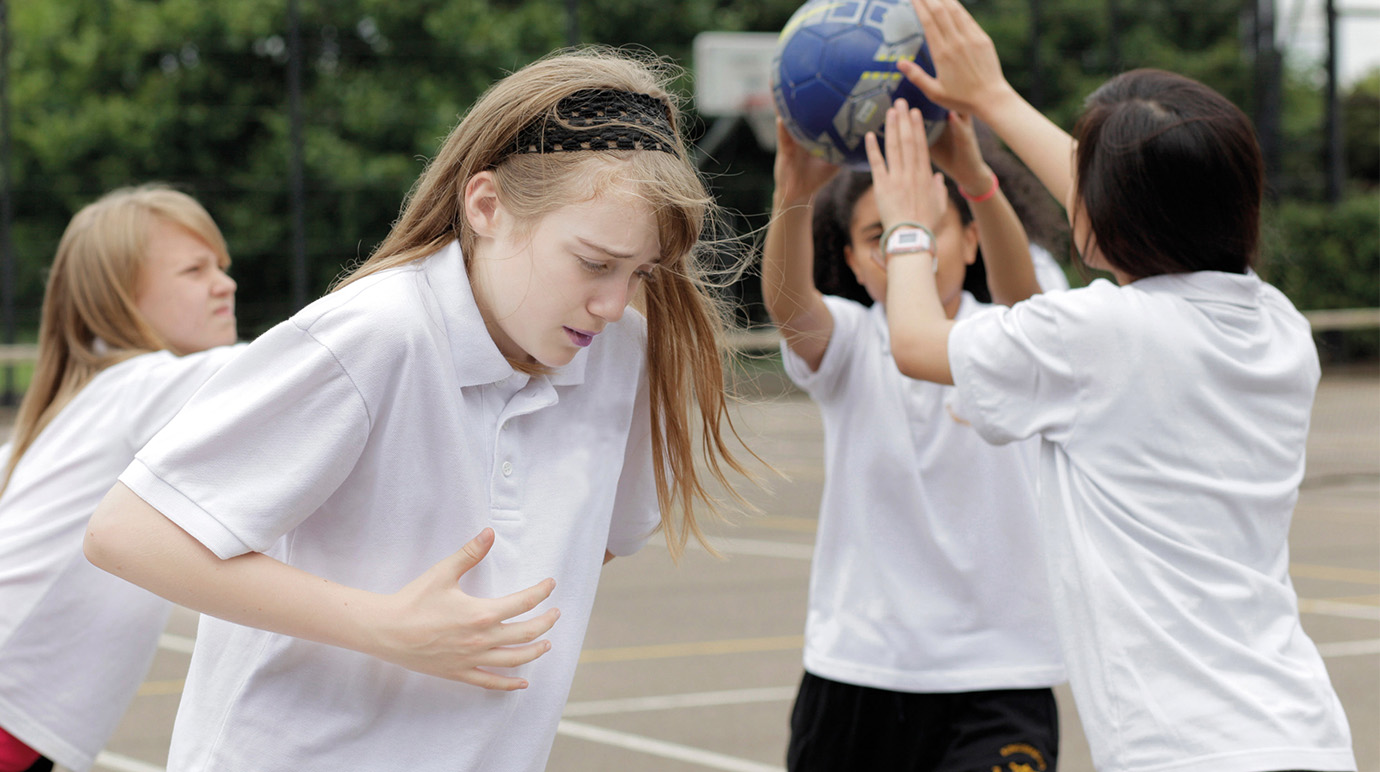

In adults and children, a severe asthma attack or flare can cause hypoxia. At the time of an attack, your airways become narrow and this makes it hard to get into lungs. As you cough to clear your lungs, more oxygen is used and symptoms aggravate.
Hypoxia may also be caused due to:
-
Lung damage because of trauma
-
Heart problems
-
Suffocation
-
Strokes, epilepsy and cervical neck fractures
-
Muscle weakness
-
Intense exercise
-
Anemia (lowered red blood cells that carry oxygen)
-
Cirrhosis
-
Lung diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),emphysema,bronchitis, pneumonia,and pulmonary edema
-
Powerful pain medicines and several other drugs that have respiratory effects
-
Cyanide poisoning
-
Aging
-
Central sleep apnea
-
Anaesthetics
-
Anatomical or physiological shunting
Signs And Symptoms
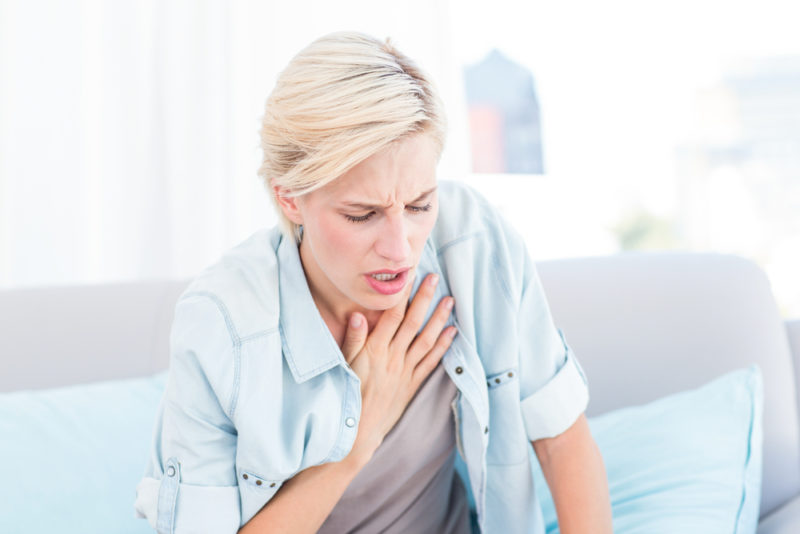

The signs and symptoms of hypoxia/hypoxemia may vary from person to person. Here are some of the most common ones:
-
Rapid breathing
-
Insufficient alveolar ventilation
-
Sweating
-
Confusion
-
Cough
-
Cyanosis
-
Shortness of breath
-
Wheezing
-
Change in skin color, ranging from blue to cherry red
-
Fast heart rate
-
Digital clubbing
-
Hemoptysis
How Can It Be Prevented?
The best way of preventing hypoxia is by keeping asthma under control every day. Strictly follow your asthma treatment plan. Some other preventions include:
-
Eating right and staying active.
-
Identifying the asthma triggers and finding ways of avoiding them.
-
Taking medicine to help prevent flares and the need to use your rescue inhaler.
-
Working with the doctor to come up with an action plan for asthma attacks so that you know how to deal with troubled breathing.
How To Treat It?
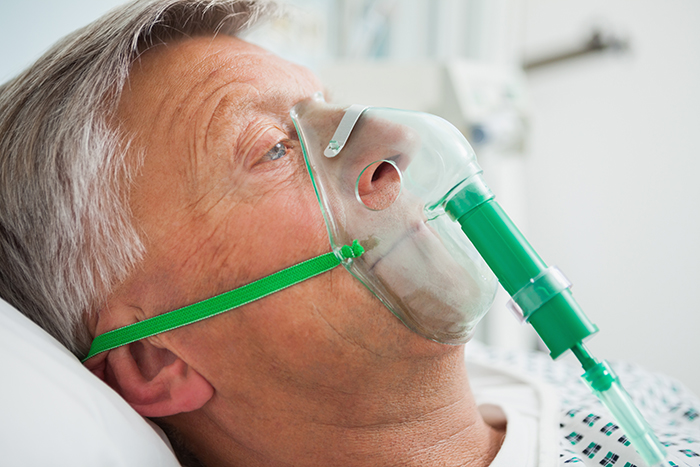
A hospital visit is required for treatment for hypoxia. Also, keep a check on your oxygen level. What’s most important is to get more oxygen inside your body. A small plug in the mouth or a mask covering nose and mouth can help in transmitting oxygen inside the body. It is enough to bring oxygen level to normal in case of many people. To make the breathing easier, an inhaler or asthma medicine also works.
If any of these don’t work, the doctor might try to give you medicine through a vein in your arm. You may also need steroid drugs for a short while in order to reduce inflammation in lungs. And when the condition is severe and other treatments don’t work, you may need a machine for breathing.
Image Source:
1. firstaidforyoung
2. stackpathdns
3. knowmore