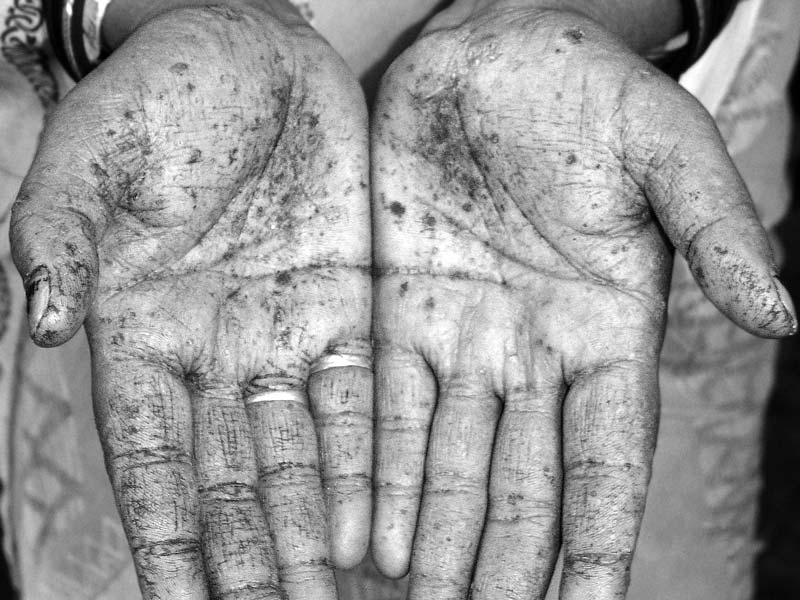
Arsenicosis, also known as arsenic poisoning, is a waterborne disease that results from drinking water containing highly dangerous levels of arsenic over a long time. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), the recommended limit of arsenic in drinking water is not more than 0.01 mg/l.
Arsenic is a natural semi-metallic chemical found in different parts of the world usually in sources such as contaminated groundwater, arsenic-preserved wood and infected soil and rock. Its effects on health may be delayed and its long-term exposure can gradually cause several health disorders including skin problems, kidney, bladder and lung cancer and many others.
It can lead to major health complications and even death if not treated. This chronic illness must be prevented among people who are at high risk and the most effective way of prevention is consuming drinking water that has low arsenic concentration.
Let’s look at the causes, symptoms, complications, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of arsenicosis here.
Causes
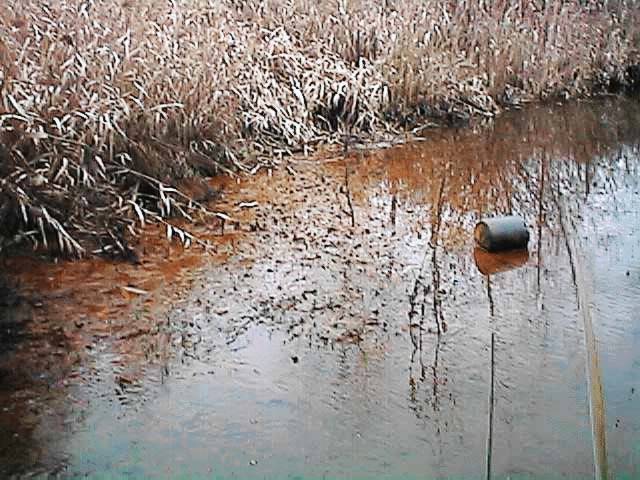

Arsenicosis is caused by a naturally occuring chemical and toxic element called arsenic that is not beneficial for human health. The natural arsenic salts are present in all the waters sources around world in very small concentrations mostly less than 0.01 mg/l.
With long-term exposure to arsenic in contaminated drinking water, food or air (absorption, inhalation and swallowing). The industrial processes like mining, metal refining and others contribute to arsenic contamination in water and chronic poisoning. In case of malnutrition, the effects of arsenic may worsen in the blood vessels.
The natural arsenic contamination is a major cause of arsenicosis and is prevalent in various countries of the world including China, US, Argentina, India, Thailand, Mexico, Chile, Bangladesh and others.
If arsenic contaminated water is consumed in large amounts, it can quickly cause death of the affected individual. Drinking groundwater containing high levels of arsenic toxin is the major cause of arsenic poisoning worldwide. The water gets contaminated underground by the rocks which release arsenic.
According to the WHO, over 200 million across the world are exposed to water containing potentially hazardous levels of arsenic. Also, the lack of proper safety measures can cause workers in some industries (smelting, wood treatment, glass production, pesticides production and use) may experience high risk of arsenic toxicity.
The traces of arsenic can also be found in certain foods such as fish, meat and poultry. In normal cases, the poultry contains the highest level of arsenic because of the antibiotics present in the chicken feed. Also, the rice has been found to be containing higher levels of arsenic than water.
Signs & Symptoms
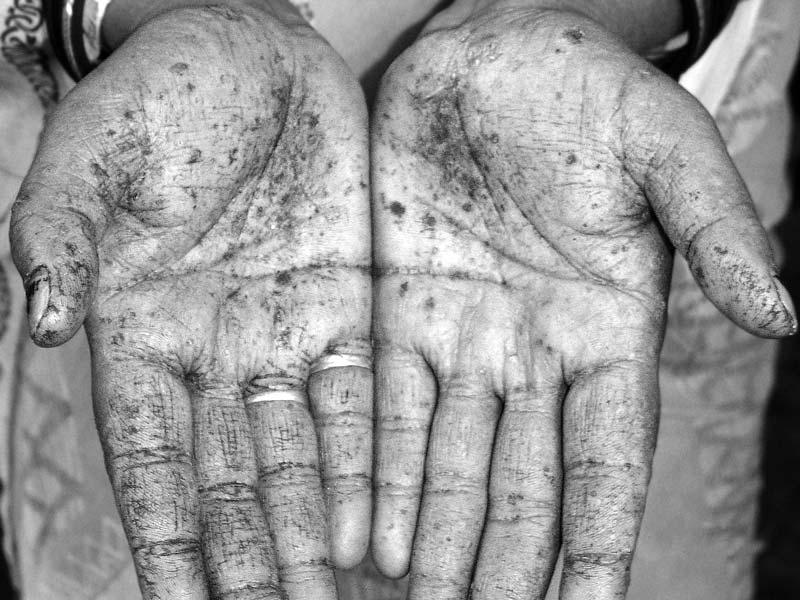
The signs and symptoms of arsenicosis may be acute or severe and immediate or chronic in which health damage is experienced for a longer time. This usually depends on the method of exposure.
An individual who has consumed food or water containing water may show these symptoms:
- Drowsiness
- Headache
- Confusion
- Severe diarrhea
If the arsenic has been or a less concentrated amount has been swallowed, the symptoms may take long time to develop. As the arsenic poisoning develops, the affected individual may begin to experience convulsions and the finger pigmentation may change.
In severe cases, the symptoms of arsenicosis include:
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Hair loss
- Excess saliva
- Metallic taste in the mouth and garlicky breath
- Stomach cramps
- Blood in the urine
- Convulsions
- Cramping muscles
- Excessive sweating
- Problem in swallowing
The arsenic poisoning usually affects the liver, kidneys, skin, and lungs. In the final stage, the symptoms are seizures and shock which may eventually lead to coma or death.
Complications
The complications associated with long-term consumption of arsenic are:
- Liver disease
- Cancers of skin, kidney, bladder, and lung
- Skin & digestive problems
- Diabetes
- Nervous system complications like loss of sensation in the limbs and hearing issues
- Disease of legs and feet blood vessels
- High blood pressure
- Reproductive disorders
Diagnosis

The diagnosis of arsenicosis depends on both clinical as well as laboratory tests. But it can primarily be diagnosed based on the cutaneous signs which include keratosis, melanosis and skin cancers. The trained dermatologists or arsenic experts can even confirm the disease clinically without even laboratory assistance.
Even though the systemic signs are not considered as diagnostic indicators, they are an important telltale signs in reaching the diagnosis. The pathological testing can help in confirming the case of arsenicosis. In the areas with a risk of arsenic poisoning, it’s crucial to monitor the arsenic levels in people at risk. In the places where lab facilities are available, the level of arsenic is measured in the drinking water, blood, hair, fingernails and urine.
The urine tests should be conducted in a couple of days of the initial exposure to get the correct measure of when the poisoning took place. These tests can also be used for diagnosing cases of apparent arsenic poisoning. The tests conducted on fingernails or hair show the level of arsenic exposure over a year but don’t tell about the possible effects on an individual’s health.
The newer biomarkers of arsenic exposure are being found out to provide information on arsenic poisoning at an early stage. The urinary porphyrin level, blood metallothionein have shown encouraging results.
Treatment
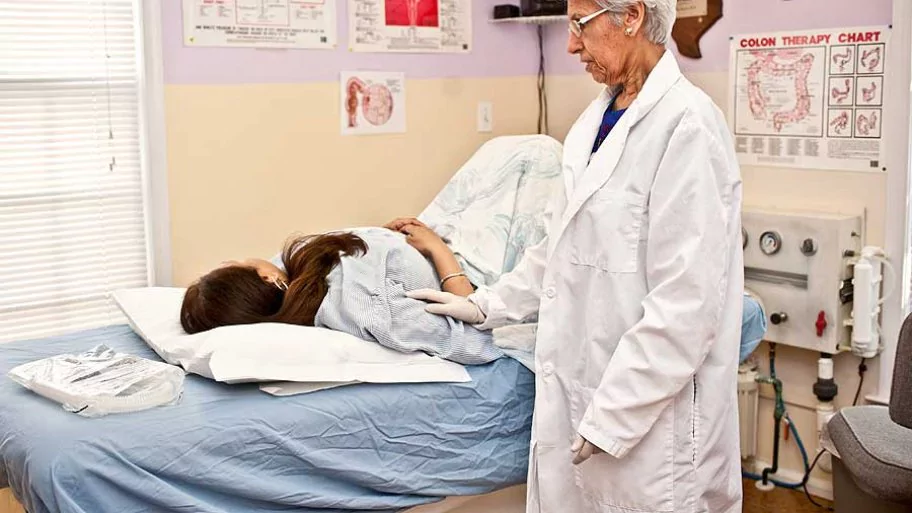
The treatment of arsenicosis depends on the type and stage of arsenic poisoning that the affected person has. Some of the methods help in removing arsenic from the human body before they end up causing damage. The other methods help in repairing or minimizing the damage the already caused damage.
The treatment methods of arsenicosis are:
- Blood transfusions
- Washing and rinsing the affected skin well
- Use mineral supplements which help in lowering the risk of potentially lethal heart rhythm problems by observing the kidney function
- Bowel irrigation is a medical process in which a special solution is passed through the gastrointestinal tract and its contents are flushed out. This helps remove arsenic and prevents its absorption into the gut.
- Chelation therapy is a treatment in which certain chemicals such as dimercaptosuccinic acid and dimercaprol are used for isolation of arsenic from blood proteins.
- Take heart medication in case of heart failure
Some non-specific therapies like keratolytics for hyperkeratosis serve as palliative measures. The affected people require follow-ups at regular intervals for detecting any onset of cancers at the earliest stage possible. The counseling, educational seminars and public awareness can be advantageous for mitigation measures.
Preventions

The problem of arsenicosis can be prevented based on several factors and the most important of all is stopping the intake of arsenic-contaminated water. Here are some key preventive measures to take for arsenicosis:
- Rainwater harvesting in high-rainfall areas, ensuring that the water collection process doesn’t pose the risk of infection or turns into a breeding ground for the mosquitoes.
- Water testing to keep a check on traces of arsenic or arsenic levels and notifying people using the water
- Adopting arsenic removal systems (arsenic removal plants or arsenic treatment units) in the households for treatment of surface water and before distributing water in the piped systems
- Taking depth of wells into consideration as the deeper wells tend to have lesser amount of arsenic in the water
- Traditional dug wells
- Proper nutrition and antioxidants can prevent onset of arsenicosis symptoms
- Educating people regarding the health effects of arsenicosis and ways of prevention
- Monitoring the health of people and checking for any early signs of arsenicosis in the people living in endemic areas
Image Source:
1) followgreenliving
2) millenniumwaterstory
3) rdic
4) angieslist
5) nuffoodsspectrum