Arthritis causes inflammation of one or more joints. It results in swelling, pain, and stiffness the affected joint. While mostly adults get the disease, children may also have some of its forms. It can occur in any joint of the body but it’s most common in the knee.
The arthritis of the knee can make it difficult to perform several day-to-day activities like walking and stair climbing. Knee arthritis is known to be a major reason behind lost work time and a serious disability. Out of more than 100 types of arthritis, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common types that happen in the knee.
Though there’s no cure for arthritis, a lot of treatment options are available for managing the pain and allowing an active lifestyle. Here are the types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of knee arthritis.
Types of Knee Arthritis
The 3 major types of arthritis affecting the knee are osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (OA) and post-traumatic arthritis.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis or RA is a chronic type of knee arthritis in which multiple joints of body are attacked throughout the body, especially joint. This symmetrical disorder mostly affects joints on both sides of the body. In this condition, the synovial membrane covering the knee joint starts swelling up, causing stiffness and knee pain.
An autoimmune disease, the immune system attacks and damages the normal tissues like cartilage and ligaments and softens the bone.
- Post-traumatic arthritis
This form of arthritis develops post a knee injury. Post-traumatic injury may occur when a broken bone damages the joint surface and results in arthritis years after surgery. Ligament injuries and meniscal tears can lead to instability and additional wear-and-tear on knee joint which can cause arthritis in later years.
- Degenerative arthritis or Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. This degenerative, wear-and-tear form of arthritis occurs mostly in people of and over 50 years of age but can happen in younger people as well.
The cartilage in the knee joint wears down slowly. The wearing down of cartilage causes it to become rough and frayed and the protective space between the bones are decreased and painful bone spurs are produced. OA develops gradually and its pain aggravates with time.
Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
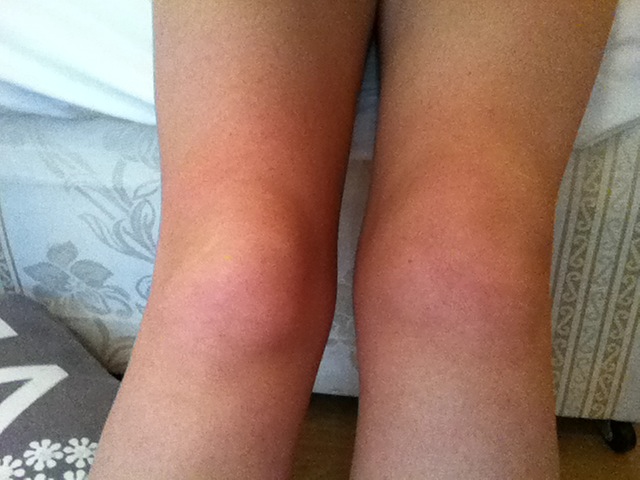
When a knee joint is affected by arthritis, it may feel painful and inflamed. The pain usually develops over time; however, a sudden onset may also occur. Other symptoms also take place such as:
- Gradual worsening of pain
An arthritis pain can start suddenly but there are more chances of developing slowly. Initially, the pain may be noticed in the morning or after long period of inactivity. The knees may feel the ache while walking, climbing stairs, standing up from a sitting posture, or kneeling down.
Pain may also be felt when you just sit down. Some people also believe that damp weather or other weather changes can cause pain. A knee pain that wakes you up from sleep can be a symptom of OA.
- Buckling and locking
In course of time, the knee muscles may become weakened and the whole joint structure can turn unstable. The overall weakness in the knee causes it to buckle. The joint can stick or lock up so that you cannot bend it or straighten out.
- Swelling, tenderness and inflammation
The knee arthritis may cause inflammation because of the bone spur formation (osteophytes) or extra fluids in knee. The swelling may be more prominent after long hours of inactivity. The skin on knee may feel warm or appear red to the touch. Over a period of time, chronic knee inflammation may occur that does not improve even with OTC (over the counter) meds or anti-inflammatory drugs.
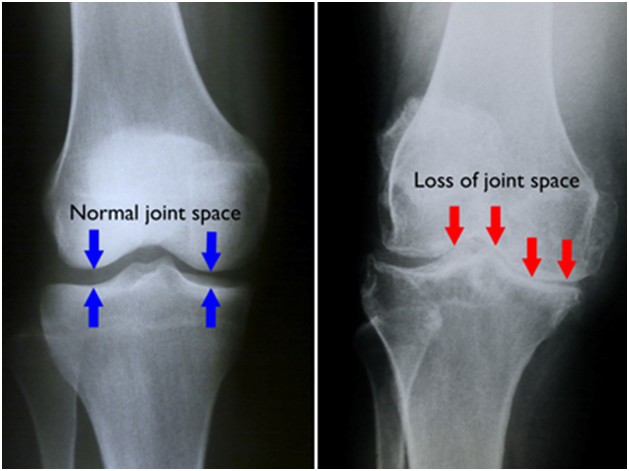
- Loss of joint space due to bone spur formation
The knee X-rays are a great tool for diagnosis as they demonstrate the loss of joint space which is causing sound and poor range of motion. The space that is usually occupied by cartilage wears away and the exposed bone is present. The bone spurs tend to develop along the joint edges and reflect body’s attempt to self-repair. That’s a common symptom of OA.
- Grinding sensation, cracking or popping sounds
While moving, grinding sensation (crepitus) may be felt in the knees. Cracking or popping sounds may even come from your knees. These symptoms may occur when you may have lost some smooth cartilage that aids in smooth range of motion. If you have knee arthritis, the grinding and noises result from rubbing of bone spurs and rough surfaces against each other while moving the joints.
- Deformities in the knee
When the arthritis advances, certain changes may be noticed in the appearances of your knee. This condition may create a hollowed appearance as the muscles around the knees become weak and thin. Your knees may start pointing outward or toward each other. The knee deformities may be hard to notice or severe or debilitating.
- Limited range of motion
The knee arthritis can make it really difficult for the joints to glide like they should, making even simple movements impossible or difficult. A limited range of motion can be noticed while climbing stairs or performing athletic activities.
How To Diagnose If You Have Arthritis Of The Knee?
At the time of physical examination, your doctor will look for various symptoms such as grating sensation, trouble walking, warmth, redness, pain, injury, tenderness, and swelling in the knee joint. Some of the imaging and laboratory tests include:
Imaging Tests
-
X-rays present detailed pictures of dense structures like bone. They can help in differentiating among different types of arthritis. An arthritic knee narrowing of joint space, osteophyte formation and bone changes.
-
Other tests include a computed tomography (CT) scan, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, or a bone scan. They help in determining the condition of the bone and soft tissues of your knee.
Lab tests
Blood tests may also be recommended for determining the arthritis type. Certain forms of arthritis including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) can be properly diagnosed with blood tests.
Treatment (Natural, Medicinal & Surgical)

Some types of exercises can help in sustaining knee function and relieving pain, including strength training, water aerobics and tai chi. Weight loss can help in relieving OA as pressure on knee would be reduced.
According to some studies, supplements like glucosamine, avocado soybean unsaponifiables (ASU), turmeric, chondroitin sulfate, capsaicin may help relieve inflammation and pain caused due to knee arthritis.
If doctor prescribes, take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for they can help in providing temporary relief in arthritis pain and reducing inflammation in knee joint. Other meds include disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), corticosteroids, analgesics and biologic response modifiers.
The injections that help in knee arthritis are hyaluronic acid supplements, corticosteroid injections, and arthrocentesis.
Surgery may also be suggested if other treatments do not help in pain and other symptoms. The most common surgeries for knee arthritis are:
-
Total joint replacement (arthroplasty) is the most common type. In this procedure, the doctor replaces the knee with a prosthetic made of plastic, ceramic, or metal.
-
Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure in which the doctor makes a cut in the knee for removal or repair of damaged parts.
-
Osteotomy involves modifying knee bones for controlling damage and pressure in the knee.
Some other surgical procedures are cartilage grafting and synovectomy.
Consult a doctor regarding the treatment or procedure that would be best for you depending on the level of pain, its effect on daily activities and amount of damage to knee.
Image Source:
1) express
2) wordpress
3) orthosurgeon
4) healthline

