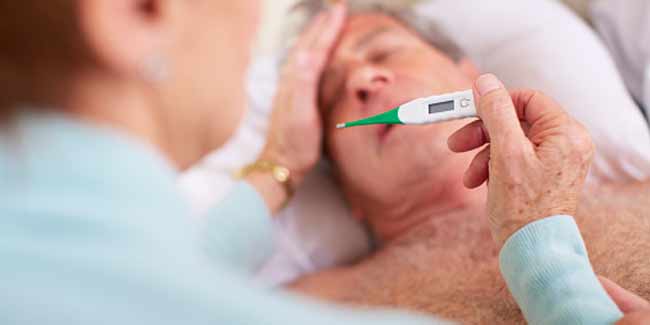
Dengue (pronounced deng-ee or deng-gey) fever, also called breakbone fever or simply dengue, is a mosquito-borne disease prevalent in the tropical and subtropical areas of the world that causes severe flu-like symptoms. A mild form of dengue leads to rash, high fever, joint pain and high fever. Its severe form, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever, can result in dangerously low blood pressure (shock) and even death.
This painful, debilitating condition is caused by four different closely related dengue viruses (that cause West Nile infection & yellow fever) and transmitted through the bite of Aedes mosquito. It cannot spread directly from person to person. The best way to control it is preventing the mosquito breeding in open water sources and covering the standing water.
Let’s take a look at the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of dengue fever.
Causes
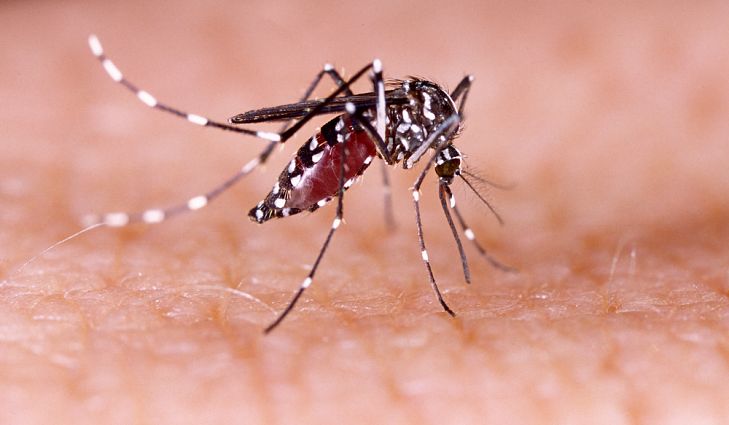
Dengue fever is caused by any of the four different types of dengue viruses which get transmitted through mosquitoes thriving in artificial water containers with close proximity to human habitation (where they prefer to lay eggs). This makes it a form of waterborne disease.
When a mosquito bites a person who is infected by dengue virus, this virus enters inside the mosquito. And when that infected mosquito bites another person, the virus gets into the bloodstream of that person.
After you recover from dengue fever, you become immune to the virus you get infected by but not the other three dengue viruses. So if you get infected again and again, you are at a risk of developing severe dengue fever (dengue hemorrhagic fever) increase.
Another risk factor of developing dengue or severe dengue is living in tropical or subtropical regions including southeast Asia, western Pacific islands, Latin America and the Caribbean.
Signs & Symptoms
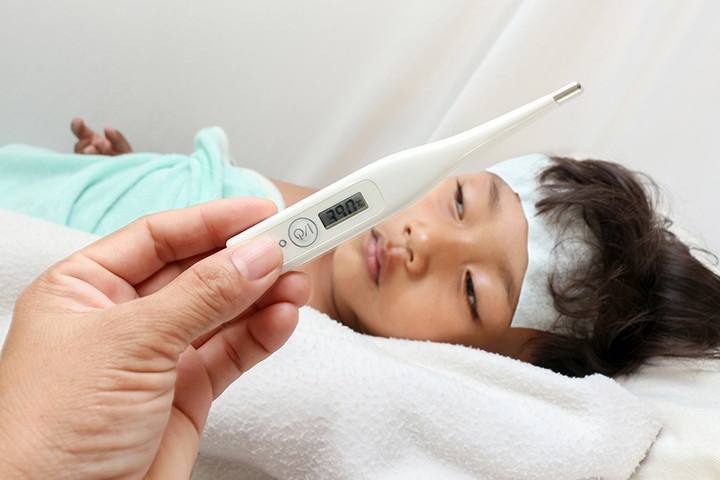
In mild cases of dengue fever, the people particularly children or teens may have no signs. And when they do come, they usually start 4-7 days after the infection and can last upto 10 days.
These signs include fatigue, vomiting, pain behind the eyes, nausea, severe joint, bone and muscle pain, severe headache, skin rash, swollen glands, mild bleeding and sudden high fever.
The symptoms are mild sometimes and can be confused with flu or some other viral infection. The people mostly recover within a week. The younger children who never had the infection previously have milder cases than older children and adults but a serious case may develop.
The serious form of dengue fever, called dengue hemorrhagic fever, is its rare complication. In this condition, high fever, difficulty breathing, severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting (may be bloody), irritability or restlessness, liver enlargement, bloody bowel movements, damaged and leaky lymph and blood vessels, nose and gum bleeding and circulatory collapse may occur.
These symptoms may progress to bleeding, shock and even death. And this is called dengue shock syndrome (DSS). The people who have weakened system and have been infected by dengue virus more than once are at a higher risk of developing dengue hemorrhagic fever.
Diagnosis

It can be hard to diagnose dengue fever as its signs and symptoms are similar to that of malaria, typhoid fever and leptospirosis. Your doctor might enquire about your medical and travel history.
Make sure you give the details to the doctor such as exposure to mosquitoes and the visited countries (to find out whether these countries have large mosquito population or dengue viruses). Some lab tests can help in detecting the presence of dengue virus. A blood test may be carried out for checking the presence of virus or antibodies.
Treatment

No specific treatment is there for dengue infection. As you recover from dengue fever, you might have signs and symptoms of dehydration due to high fever and vomiting. So have a lot of fluids and see a doctor if you experience any of these:
- Decreased urination
- Dry mouth or lips
- Cold or clammy extremities
- Few or no tears
- Lethargy or confusion
To reduce the pain and fever, your doctor may prescribe you pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol, others). And you must avoid pain relievers that aggravate bleeding like aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve, others).
If you have severe dengue fever, you may require supportive care in a hospital, intravenous (IV) fluid and electrolyte replacement, blood pressure monitoring and transfusion to replace blood loss.
Moreover, you should take enough rest and drink plenty of fluids. If you feel even worse in the first 24 hours once your fever gets lower, contact a doctor right away and visit a hospital to check for any complications.
Image Source:
1. worldatlas
2. momjunction
3. onlymyhealth
4. healthline