Sinus infection or sinusitis results from the inflammation or swelling of the tissue along the sinus. While the healthy sinus is filled with air, the infected one gets clogged or filled with fluid due to growth of germs causing an infection. The conditions causing sinus blockage include common cold, allergic rhinitis, nasal polyps and deviated septum.
Types of sinusitis are acute sinusitis (usually starts with cold-like symptoms, may start suddenly and last 2-4 weeks), subacute sinus inflammation (usually lasts 4-12 weeks), chronic inflammation symptoms (last 12 weeks or longer) and recurrent sinusitis happens several times a year.
Here are the signs and symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment methods for sinus infection.
Signs & Symptoms

It is common to have sinusitis after cold or flu. Here are the signs and symptoms of sinus infection:
-
Blocked nose
-
Toothache
-
Reduced sense of smell
-
Thick green or yellow nasal discharge
-
Runny nose or discolored postnasal drainage
-
Bad breath
-
Feeling of congestion or fullness in face
-
Pus in nasal cavity
-
Fatigue
-
Stuffed up nose
-
Fever
-
Pain, swelling and tenderness around eyes, forehead and cheeks
In young children, the signs of sinusitis include difficulty eating, irritability and breathing through mouth.
Causes
Sinus infection could be triggered by or caused due to:
-
Nasal polyps
-
Cigarette smoking or second hand smoke
-
Fungus, bacteria and viruses
-
Sensitivity to aspirin
-
Swelling inside the nose like that from a common cold
-
Blocked drainage ducts
-
Immune system deficiencies or medications suppressing the immune system
-
Hormonal conditions, including those occurring in pregnancy
-
Asthma and other lung disorders, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
-
Genetic disorders that lead to impairment of cilia
-
Changes in air temperature or air pressure
In children, causes of sinusitis include:
-
Pacifiers
-
Illnesses from other kids at daycare or school
-
Smoke in the environment
Diagnosis
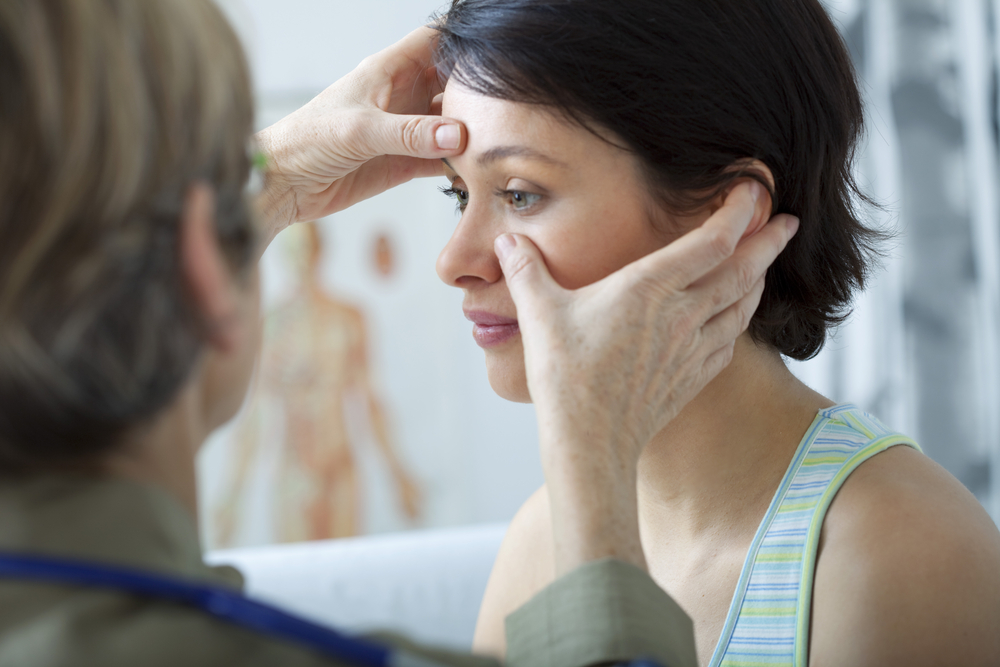

The diagnosis depends on symptoms and requires throat, nose and sinus to be examined. An allergist will check you out for tenderness of face, redness, bad breath, discolored (greenish) nasal discharge and swelling of the nasal tissues.
If sinus infection tends to last longer than 8 weeks or if standard antibiotic treatment doesn’t seem to work, a sinus CT scan may could help allergist in diagnosing the problem. Your nose or sinus openings could be examined. A long, thin, flexible tube with a tiny camera and a light at one end is used for insertion in the nose.
If you have a chronic sinus infection that hasn’t improved since long, a mucus culture could be helpful in determining what is causing the infection. Most of the mucus samples are taken from the nose. However, it is sometimes crucial to obtain mucus (or pus) directly from the sinuses.
By finding out what type of bacteria is causing the infection can lead to better and effective antibiotic therapy. A fungus may also be causing your sinus infection and it’s important to confirm its presence.
Your allergist may ask you to go through a sinus CT. This test can help in defining the extent of the infection. Your allergist may also ask you to go to an allergy and immunology expert. These experts will check for key factors such as allergies, asthma, structural defects, or a weakness of the immune system.
Biopsies that involve sinus tissue are taken using flexible instruments inserted through the nose. The biopsies of the sinus tissue are also used for testing immotile cilia syndrome, a rare disorder that can cause people to suffer from recurrent infections such as chronic sinus infection, bronchitis and pneumonia.
Treatment

Here’s how mild sinusitis can be treated by yourself:
-
Cleaning nose with salt water sprays (neti pots) for relieving congestion
-
Take good amount of rest
-
Drink plenty of fluids
-
Inhale steam from bowl of hot water
-
Hold a warm clean flannel over your face for few minutes many times each day
-
Take over-the-counter painkillers such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Other than these home remedies, a doctor may recommend you these medicines:
-
Decongestant nasal sprays, drops or tablets for unblocking your nose
-
Salt water nasal sprays or solutions will help in rinsing out the inside of your nose
The nasal sprays can be bought without a prescription, but they should not be used for over a week. Some of the decongestant tablets also comprise
paracetamol or ibuprofen. If you take painkillers and decongestants too, be careful about not taking dose more than is recommended.
Image Source:
1) ehowcdn
2) sinussurgeryprocedure
3) nysinuscenter
4) theappside

